British Columbia
|
|
Template:Canadian province or territory
British Columbia, or simply B.C. (French: la Colombie-Britannique) is the westernmost of Canada's provinces. It was the sixth province to join Confederation (in 1871). As of 2004, the population was 4,168,123 (British Columbians).
| Contents |
Geography
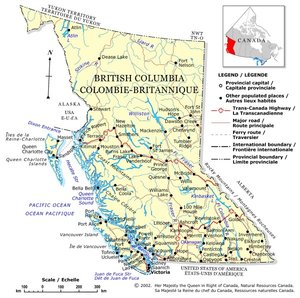
Its capital is Victoria, at the southeast of Vancouver Island. Its most populous city is Vancouver, which is in the southwest corner of the mainland of Canada (the city is not on Vancouver Island). Other major cities include Surrey, Burnaby, Coquitlam, Richmond, Delta, and New Westminster in the Greater Vancouver Regional District (GVRD), Abbotsford and Langley in the Fraser Valley Nanaimo on Vancouver Island, and Kelowna and Kamloops in the "Interior." Prince George is the major city nearest the centre of the province; however, a small town called Vanderhoof, 100 km to the west, is much nearer the geographic centre.
British Columbia is on the extreme west of Canada, on the Pacific coast. It is bound on the northwest by the U.S. state of Alaska, directly north by Yukon and the Northwest Territories, on the east by Alberta, and on the south by the states of Washington, Idaho, and Montana. The southern border of British Columbia was established by the 1846 Oregon Treaty.
The Canadian Rockies and the Inside Passage's fjords provide some of British Columbia's renowned and spectacular scenery, which forms the backdrop and context for a growing outdoor adventure and ecotourism industry. The Okanagan area is one of only three wine-growing regions in Canada and produces excellent ciders, but exports little of either drink. The small rural towns of Penticton, Oliver, and Osoyoos have some of the warmest summer climates in Canada and provide hospitality to visitors from around the world.
Much of Vancouver Island is covered by a temperate rain forest, one of a mere handful of such ecosystems in the world (notable others being on the Olympic Peninsula of Washington and in Chile. More northerly portions of the province's mainland have snowy, cold winters; however, southern portions and Vancouver Island are temperate in many places, where the climate is moderated by the Pacific Ocean. In the interior, summer temperatures can be quite warm, even notably hot. There is more than one spot in British Columbia that has recorded peak summer temperatures of 43.3°C (110°F).
Ten Largest Municipalities by population
| Municipality | 2001 | 1996 |
|---|---|---|
| Vancouver | 545,671 | 514,008 |
| Surrey | 347,825 | 304,477 |
| Burnaby | 193,954 | 179,209 |
| Richmond | 164,345 | 148,867 |
| Abbotsford | 115,463 | 104,403 |
| Coquitlam | 112,890 | 101,820 |
| Saanich | 103,654 | 101,388 |
| Delta | 96,950 | 95,411 |
| Kelowna | 96,288 | 89,422 |
| Langley Township | 86,896 | 80,179 |
Parks and Protected Areas
There are 14 designations of parks and protected areas in the province that reflects the different administration and creation of these areas in a modern context. There are 141 ecological Reserves, 35 provincial marine parks, 7 Provincial Heritage Sites, 6 National Historic Sites, 4 National Parks and 3 National Park Reserves. 12.5% (11.4 million hectares) of BC is currently considered 'protected' under one of the 14 different designations that includes over 800 distinct areas.
British Columbia contains seven of Canada's national parks:
- Glacier National Park
- Gulf Islands National Park Reserve
- Gwaii Haanas National Park Reserve and Haida Heritage Site
- Kootenay National Park
- Mount Revelstoke National Park
- Pacific Rim National Park Reserve
- Yoho National Park
BC also contains a large network of provincial parks, run by BC Parks (http://wlapwww.gov.bc.ca/bcparks/) of the Ministry of Water, Land and Air Protection.
Recreation
Given its varied mountainous terrain and its coasts, lakes, rivers, and forests, British Columbia has long been enjoyed for pursuits like hiking and camping, rock climbing and mountaineering, hunting and fishing.
Much of the province is wild or semi-wild, so that populations of very many mammalian species that have become rare in much of the United States still flourish in B.C. Watching animals of various sorts, including a very wide range of birds, has also long been popular. Bears (grizzly and black) live here, as do deer, elk, moose, caribou, big-horn sheep, mountain goats, beavers, muskrat, coyotes, wolves, eagles, ospreys, herons, Canada geese, swans, loons, hawks, owls, ravens, and many sorts of ducks. Smaller birds (robins, jays, grosbeaks, chickadees, etc.) also abound. Healthy populations of many sorts of fishes are found in the waters (including, of course, salmonids such as several species of salmon, trout, char, etc.).
Cross-country and telemark skiing are much enjoyed, and in recent decades high-quality downhill skiing has been developed in the Coast Mountain range and the Rockies, as well as in the southern areas of the Shuswap Highlands and the Columbia Mountains. Snowboarding has mushroomed in popularity since the early 1990s. The 2010 Winter Olympics downhill events will be held in Whistler, B.C., while the indoor events will be in the Vancouver area.
Water sports, both motorized and non-motorized, are enjoyed in many places. Sea kayaking opportunities abound on the B.C. coast with its fjords. Whitewater rafting and kayaking are popular on many inland rivers. Sailing and sailboarding are widely enjoyed.
In Vancouver and Victoria (as well as some other cities), opportunities for joggers and bicyclists have been developed. Cross-country bike touring has been popular since the ten-speed bike became available many years ago. Since the advent of more robust mountain bikes, trails in more rugged and wild places have been developed for them. Some of the province's retired rail beds have been converted and maintained for hiking, biking, and cross-country skiing.
Of course, British Columbians have not failed to enjoy all the common sports, like golf, tennis, soccer, hockey, softball, basketball, curling, and so on. Most communities of several thousand people or more have developed facilities for these (as, in some cases, have communities of even a few hundred).
Consistent with both increased tourism and increased participation in diverse recreations by British Columbians themselves has been the proliferation of lodges, chalets, bed and breakfasts, motels, hotels, fishing camps, and park-camping facilities in recent decades.
In certain areas, there are businesses, non-profit societies, or municipal governments dedicated to promoting ecotourism in their region.
Politics
BC has a 79-member elected Legislative Assembly, elected by the First Past the Post system.
Politically, British Columbia has tended to swing between right and left, with little middle ground. Within Canada, BC is viewed much as California is in the United States, prone to unusual politics and scandals. Currently it is governed by the more conservative British Columbia Liberal Party under Gordon Campbell. However, for a decade before, it was led by the left-wing NDP. Before that, the government was led by the right-wing Social Credit Party for many years, but in the early 1990s the party collapsed due to scandal.
Recall and Initiative
British Columbia is the only province in Canada with recall election and initiative legislation.
Only one recall petition was ever deemed to have had any success, compelling MLA Paul Reitsma to resign his seat hours before he would have been removed from office.
Electoral Reform
A Citizens' Assembly in 2004 recommended replacing the First Past the Post system with a Single Transferable Vote system to be implemented in 2009, and a referendum was held on May 17, 2005 to determine if this change should go ahead. The referendum nearly passed with 57% of the popular vote of the 60% required. The second requirement was a simple majority in 60% of the current ridings and 77 of the 79 ridings achieved this, far more than the 48 minimum. The close result has provoked further interest in electoral reform.
See also: List of British Columbia general elections
History
Main article: History of British Columbia
From 1818 to 1846, British Columbia south of 54°40' and west of the Rocky Mountains was part of the Oregon Country. The land was under the control of the Hudson's Bay Company, and was divided into the departments of Columbia (south of the Columbia River) and New Caledonia (north of the river).
In 1846, the Oregon Treaty divided the territory along the 49th parallel to Georgia Strait, with the area north of this boundary (and all of Vancouver Island) becoming exclusively British territory. Vancouver Island became a Crown colony in 1849.
In 1858, in response to the Fraser Canyon gold rush, the mainland portion of the former Oregon Country was organized into the colony of British Columbia. The Cariboo region ("Central Interior") of British Columbia experienced a gold rush in the years 1862 to 1865. This created a rapid influx of miners and settlers, about 30,000 in all. The colonial authorities feared the gold rush might spread beyond B.C.'s northern border (54°40' north), so the Stikine Territory was created in 1862. However, the following year this new territory was disestablished, most of its area going to B.C., whose northern limit was increased to its current location, 60° north.
This period in the province's history is acknowledged today in the Gold Rush Trail: historic and other sites along the route from Lillooet to Barkerville and beyond. Some of the towns along this route are numbered according to their distance from the end of the navigable part of the Fraser River at Lillooet. Best known of these is the town of 100 Mile House which, along with the residential hub of 108 Mile Ranch, forms a substantial trading, tourism, and population centre for this region.
After the mainland's gold rushes collapsed and the colony almost went bankrupt from building roads in its interior, the two colonies of Vancouver Island and British Columbia agreed to merge and share the debt. The merger was effected in 1866, with the name British Columbia being applied to the newly united colony.
Several factors played in the decision of British Columbia to join Canada on 1871 July 20. These included fear of annexation to the United States, the overwhelming debt created by rapid population growth, the need for government-funded services to support this population, and the economic depression caused by the end of the gold rush. The decision was made largely because the Canadian government offered to link British Columbia to the more settled parts of Canada via the Canadian Pacific Railway and offered to pay off the $1,000,000 British Columbian debt.
The completion of the CPR was a huge boost to Vancouver, the line's terminus, and it rapidly grew to become one of Canada's largest cities. The province became a centre of fishing, mining, and especially of logging throughout the twentieth century.
In 1907, British Columbia's territory shrank somewhat after the Alaska Boundary Dispute awarded part of northwestern B.C. to the United States.
B.C. has long taken advantage of its Pacific coast to have close relations with East Asia. However, this has caused friction, with frequent feelings of animosity towards Asian immigrants. This was most manifest during the Second World War when many people of Japanese descent were interned in the interior of the province.
The post-World War II years saw Vancouver and Victoria also become cultural centres as poets, authors, artists, and musicians flocked to the beautiful scenery and warmer temperatures. Tourism also began to play an important role in the economy. The rise of Japan and other Pacific economies was a great boost to the B.C. economy.
Maps
Missing image
Bcmap.PNG
Image:Bcmap.PNG
Cities
Half of all British Columbians live in the Greater Vancouver Regional District, which includes Vancouver, Surrey, Burnaby, Coquitlam, and Richmond.
Other cities:
- Abbotsford
- Dawson Creek
- Fort St. John
- Kamloops
- Kelowna
- Nanaimo
- Prince George
- Victoria - provincial capital
- Williams Lake
See also: List of communities in British Columbia
See also
- List of British Columbia-related topics
- Canada
External links
Pacific Northwest Community (http://pnw.wikicities.com)A wiki on the Pacific Northwest
Tourism British Columbia (http://www.hellobc.com)Official Website
| Provinces and territories of Canada | 
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Regions and Regional Districts of British Columbia | 
| |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
BC Regions: Nechako | North Coast | Peace River | Cariboo | Lower Mainland | Vancouver Island/Sunshine Coast | Okanagan | Thompson Nicola | Kootenays | ||||
|
BC Regional Districts: Alberni-Clayoquot | Bulkley-Nechako | Capital | Cariboo | Central Coast | Central Kootenay | Central Okanagan | Columbia-Shuswap | Comox-Strathcona | Cowichan Valley | East Kootenay | Fraser Valley | Fraser-Fort George | Greater Vancouver | Kitimat-Stikine | Kootenay Boundary | Mount Waddington | Nanaimo | North Okanagan | Northern Rockies | Okanagan-Similkameen | Peace River | Powell River | Skeena-Queen Charlotte | Squamish-Lillooet | Stikine | Sunshine Coast | Thompson-Nicola | ||||
de:Britisch-Kolumbien et:Briti Columbia es:Colombia Británica eo:Brita Kolumbio fa:بریتیش کلمبیا fi:Brittiläinen Kolumbia fr:Colombie-Britannique he:קולומביה הבריטית io:British Columbia it:Columbia Britannica ja:ブリティッシュコロンビア州 ka:ბრიტანეთის კოლუმბია la:Columbia Britannica nl:British Columbia pl:Kolumbia Brytyjska pt:Colúmbia Britânica simple:British Columbia sk:Britská Kolumbia sv:British Columbia vi:British Columbia zh:不列颠哥伦比亚